Troubleshooting
Query String gets swallowed
When you call the API endpoint with a query string, for example /graphql/?lang=1 and that lang parameter gets swallowed by apache, it is due to the missing QSA-RewriteRule-Flag. Find the RewriteRule that looks like this:
RewriteRule ^(graphql/) widget.php?cl=graphql [NC,L]
and make it look like this:
RewriteRule ^(graphql/) widget.php?cl=graphql&skipSession=1 [QSA,NC,L]
Side-Effects due to OXID Session
To enforce that PHP session is not used by accident (by sending sid
parameter or cookie) and no unneeded PHP session is created, please ensure that
skipSession=true parameter is sent for each request. Easiest way to do this
is to extend the shop’s .htaccess file with the following lines
RewriteRule ^graphql/?$ widget.php?cl=graphql&skipSession=1 [QSA,NC,L]
Otherwise in newer GraphQL versions you will be presented with an error when sending GraphQL requests with a session id.
Maximum function nesting level is reached
When XDebug is active, request call will take a while and eventually Xdebug will detect a possible infinite loop. That is caused because GraphQL library tends to use a very deep stack. Simply increase the maximum allowed nesting level in XDebug config
xdebug.max_nesting_level=512
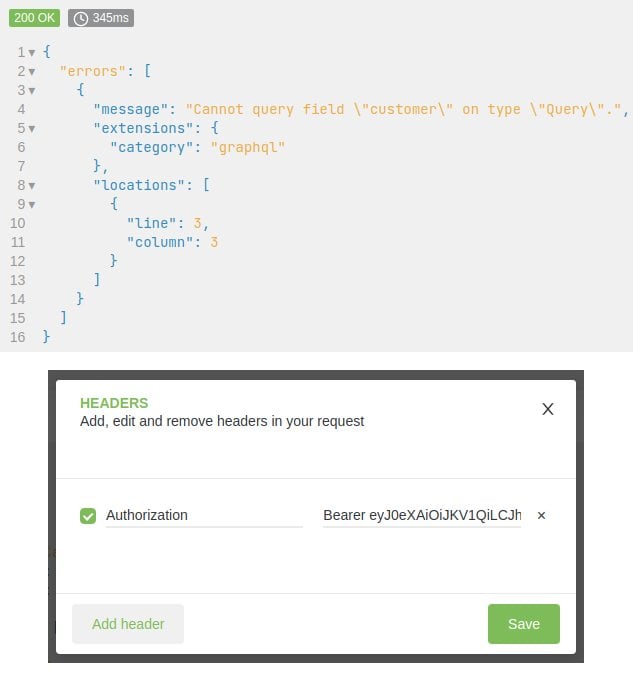
Graphql schema appears incomplete
Your client’s introspection requests get the available schema based upon your access rights. Make sure you are logged in and using the correct token in the Authorization header.
The rights are depending on the user group. If you’re having trouble finding admin panel requests, this could also be caused by insufficient account rights. If queries or mutations are missing, please check the user groups and the depending rights in the PermissionProvider-Classes of the modules.
Important
You may want to doublecheck this in the database, as the administrative dashboard setting name could be different. E.g. it could say a user has been granted admin rights, but actually they are a malladmin. It is not the same and does not give enough access to query, as an example, the shop version.
To gain admin rights, the user group oxidadmin needs to be assigned.
Installation issues for dev environment
In case you’d like to contribute, installing the modules as described in the developer documentation might lead to your changes not being reflected or errors when activating the modules.
A more reliable first step in setting things up would be to clone the desired repository in the oxideshop directory, for example, and symlink it into its respective place in source\modules like this:
cd /var/www/oxideshop
git clone <url-to-module-repository>
ln -s <module-directory-path> ./source/modules/<target-directory>
Important
The <target-directory> should be the same as the target-directory value in the module’s composer.json file, so for graphql-base-module it’s source/modules/oe/graphql-base.
After that, you can continue from step 2. Register module package in project composer.json in the docs.
Allowing Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
In case your front-end code is served on sitea.intranet and the access to the OXID GraphQL functionality is on siteb.intranet, you will need to perform cross-domain requests between sitea.intranet and siteb.intranet. This may be done using CORS headers. One way to do this is to amend the apache2/sites-enabled/*.conf file:
Define APACHE_CORS_ALLOWED_DOMAINS "sitea.intranet|siteb.intranet"
Define APACHE_CORS_ALLOWED_METHODS "POST, GET, OPTIONS"
Define APACHE_CORS_ALLOWED_HEADERS "Content-Type, Authorization"
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_METHOD} OPTIONS
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ $1 [R=200,L]
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
SetEnvIf Origin "http(s)?://(www\.)?(${APACHE_CORS_ALLOWED_DOMAINS})$" AccessControlAllowOrigin=$0
Header always set Access-Control-Allow-Origin %{AccessControlAllowOrigin}e env=AccessControlAllowOrigin
Header always set Access-Control-Allow-Methods "${APACHE_CORS_ALLOWED_METHODS}"
Header always set Access-Control-Allow-Headers "${APACHE_CORS_ALLOWED_HEADERS}"
Header merge Vary Origin
</IfModule>
Note
The above will only work in an apache configuration file, not in an .htaccess file.
For development purposes, you can also use the following, simplified, configuration in your shop .htaccess file:
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_METHOD} OPTIONS
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ $1 [R=200,L]
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_headers>
Header set Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*"
Header set Access-Control-Allow-Methods "POST, GET, OPTIONS"
Header set Access-Control-Allow-Headers "Content-Type, Authorization"
</IfModule>
Important
Keep in mind that the mod_headers and mod_rewrite must be enabled on the apache server.
# On Debian/Ubuntu, to check which modules are enabled, you can use:
apachectl -M
# You can enable mod_headers & mod_rewrite, by running:
a2enmod headers
a2enmod rewrite
# And then restart the apache server
apachectl -k graceful