Modules configuration and setup
Note
Watch a short video tutorial on YouTube: Module Installation & Configuration.
Overview
In most cases modules need to be configured before you can proceed with setup and activate it. There are two ways of configuring modules:
The automatic deployment friendly way by Configuring modules via providing configuration files
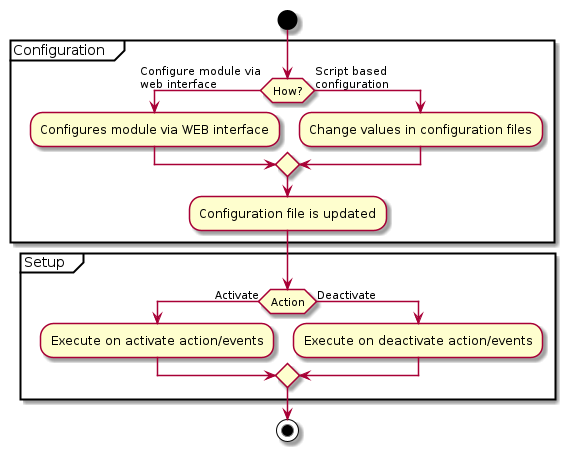
Configuration
Configuring modules via admin interface
To configure modules via admin interface, open OXID eShop administration panel and go to .
You will see a list of installed modules.
Select the module you want to configure and choose .
You will see a list of settings that you can change.
Entries in the settings list are loaded and saved in configuration files located in var/configuration/shops.
For each shop ID there is one directory with the complete configuration for this shop.
So if the shop has ID 1, a directory would be named 1. See the example below:
.
└── var
└── configuration
└── shops
└── 1
└── 2
└── ...
Note
If the var directory cannot be found in the project directory, execute composer update or create the var directory manually.
Also, each shop must have their own separate directory.
Configuring modules via providing configuration files
Since the complete configuration is in configuration files, you can make it part of the VCS repository of your project and deploy it to your testing, staging and productive systems and deploy through the command line as described below in the section deploy module configurations.
Project configuration files are located in project directory var/configuration/shops/<shop-id>/, where “<shop-id>” represents sub-shop ID. In case you don’t use sub-shop functionality, it will always be only one directory.
Each directory with a shop configuration has a class_extension_chain.yaml file with the module class extension chains and a separate subdirectory modules for module configurations. Configuration for every module is in a separate file where filename is the module id: var/configuration/shops/<shop-id>/modules/<module-id>.yaml
.
└── var
└── configuration
└── shops
└── 1
└── modules
└── oe_moduletemplate.yaml
└── ...
└── class_extension_chain.yaml
Configuration files
These files contain information of all modules which are installed.
During the installation process, all of the information from module metadata.php is being transferred to the configuration files.
For example you have OXID eShop without any modules, so var/configuration/shops/<shop-id>/modules/ will be empty.
When you will run the installation let’s say for the OXID eShop Module Template module, the files in var/configuration/shops/<shop-id>/ will be filled with information from metadata.php.
An example of stripped down configuration file var/configuration/shops/1/modules/oe_moduletemplate.yaml:
id: oe_moduletemplate
moduleSource: vendor/oxid-esales/module-template
version: 2.0.0
activated: true
title:
en: 'OxidEsales Module Template (OEMT)'
description:
en: ''
lang: ''
thumbnail: pictures/logo.png
author: 'OXID eSales AG'
url: ''
email: ''
classExtensions:
OxidEsales\Eshop\Application\Model\User: OxidEsales\ModuleTemplate\Model\User
OxidEsales\Eshop\Application\Controller\StartController: OxidEsales\ModuleTemplate\Controller\StartController
controllers:
oemtgreeting: OxidEsales\ModuleTemplate\Controller\GreetingController
events:
onActivate: '\OxidEsales\ModuleTemplate\Core\ModuleEvents::onActivate'
onDeactivate: '\OxidEsales\ModuleTemplate\Core\ModuleEvents::onDeactivate'
moduleSettings:
oemoduletemplate_GreetingMode:
group: oemoduletemplate_main
type: select
value: generic
constraints:
- generic
- personal
oemoduletemplate_BrandName:
group: oemoduletemplate_main
type: str
value: Testshop
Also, the file with the module class extension chain will be generated.
Example: var/configuration/shops/1/class_extension_chain.yaml:
OxidEsales\Eshop\Application\Model\User:
- OxidEsales\ModuleTemplate\Model\User